Data is one of the most valuable digital resources in the modern world. Companies that have access to Big Data and have enough computing facilities to effectively process and analyze it usually have a bigger market share and generate more income. Access to information gives a unique opportunity to understand the interests and demands of the customers much better and even exceed their expectations. This makes the necessity of data collection, which is the first and most important step of any decision-making process, really urgent. But before diving deeper into the topic, let’s get started with some important definitions.
What Is Data Collection?
Data collection is the process of gathering data, its further measuring, processing, assessing and analyzing for research purposes. It’s conducted with the help of established, validated techniques, which make it possible to answer research questions, test hypotheses, and evaluate final results. The main goal of data collection is to get access to reliable sources of information that will provide data for further analysis and make data-driven decisions possible.
Types of Data Collected
There are two main types of collected data.
- Qualitative data, which deals with descriptive information that cannot be counted and is not expressed through numerical values
- Quantitative data, which represents information that can be counted
- The chosen method of data collection depends on the subject matter and what information it is necessary to assess.
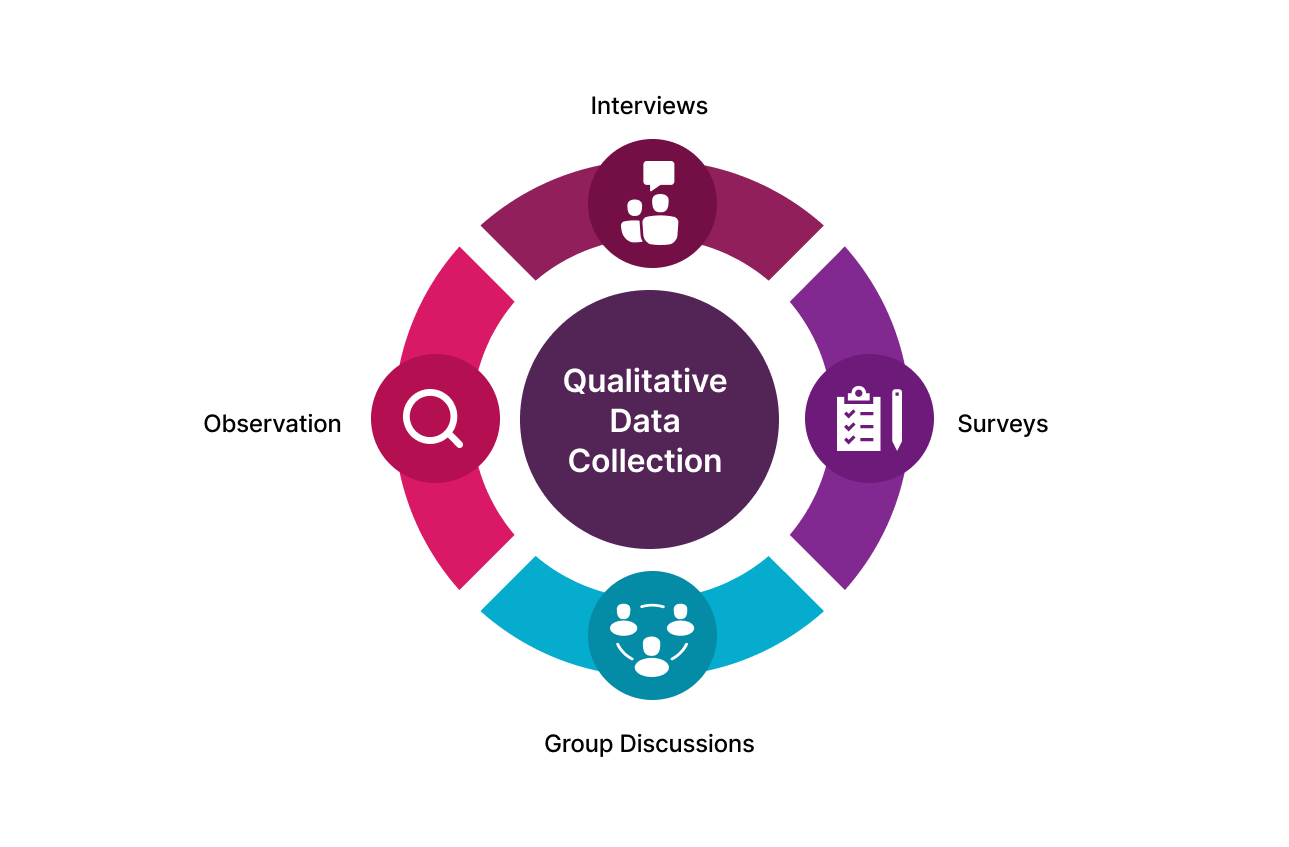
Qualitative Data Collection Methods
Qualitative data collection methods come into the limelight when it is necessary to answer the question “Why?” instead of “How many/much?” This type of data is less concrete and much more difficult to measure than quantitative data, as it usually contains descriptions and opinions on a particular topic. The methods that grant access to qualitative data include interviews, observations, product reviews, answers to open-ended questions, and others.

Quantitative Data Collection Methods
Quantitative data is built on numbers, values, and quantities. It is much more concrete than qualitative data and can be easily measured. This type of data can be gathered with the help of different algorithms and data management platforms (DMP), which count such measurable parameters as the number of users that have bought a particular product or left the cart page, how much time users spent on a website, how far they scrolled, and many others. Quantitative data, being numeric, is a perfect basis for analysis, as it is objective and reliable. Numbers don’t lie — they lead to insights for a better understanding of your audience.
Importance of Data Collection
The modern world is gradually moving to the digital space, and we are surrounded by data. Those who learn how to use it find themselves in a more favorable position than those who build their hypotheses on some other notions. Besides, businesses invest even more resources to benefit from data collection and analysis in the post-pandemic environment. COVID-19 emphasized that unexplored data improves resilience in the digital era. The initiative will remain a priority for businesses that rethink both cultural and technological aspects in 2022 and beyond. Understanding the importance of data collection is beneficial because of the following reasons.
- Data-driven decisions are much more effective for corporate strategy development.
- Access to data allows us to identify problems at earlier stages.
- Data helps to prove hypotheses right or wrong before implementing them.
- Arguments supported by data are much more accurate.
- Fast access to organized data helps to save time.
These are just the main advantages of effective data management. There are many more areas that can be improved by data collection.
How To Collect Data
Data can be collected with the help of different methods. Each of them has its own peculiarities. But data collectors follow five fundamental stages, no matter which method they choose.

Determine What Information To Collect
Any data collection process starts with understanding what type of data should be gathered, what topics it covers, what sources are going to be used, and what volumes of information are necessary. The answers to these questions are given on the basis of the goals that were set before. For example, it may be necessary to collect data about what content is the most popular on a particular website among its visitors of a particular age who made a particular action online during the last week.
Establish a Timeframe for the Process of Collecting Data
The second stage of data collection is setting its timeframe, as different research goals need different periods of assessment. Customers’ financial behavior usually demands more time for data collection and assessment, while some specific tasks may be more limited in time — especially in situations when data becomes outdated quickly.
Determine Which Method of Data Collection Will Be Used
The data collection method is the core of the whole process. To make the right choice, you have to take into consideration what you need to accomplish by the end of the research, what data will be collected and assessed, and how long the timeframe will be. The number of parameters can be huge, which makes their configuration really time-consuming.
Collecting the Relevant Data
When all the aspects of the data collection process are determined, you can start implementing the strategy. DMP is quite a useful tool for storing and organizing the collected data. In order to succeed, you have to have a clear understanding of what you are doing and follow the plan, while making corrections whenever it is necessary.

Initiating Data Analysis and Drawing Conclusions
Once the data is collected, the stage of data analysis and organization begins. This is a crucial step, as it turns raw information into useful and valuable insights — which businesses can use to enhance their operational processes, marketing strategies, and corporate decisions. There is a great number of web analytics tools that can help you with this stage. The role of data has increased during the last decade when businesses have been undergoing digital transformation. The pace of digitalization isn’t going to slow down, which urges companies to keep track of recent digital landscape trends. Here are three key trends to consider in the forthcoming year:
Supply Chains
The pandemic revealed numerous weaknesses of both national and international disrupted supply chains. It resulted in supply delays and production slowdowns. As a result, supply chain analytics becomes an essential element of any non-self-sufficient business process. The whole situation will definitely lead to diversification of suppliers and the emergence of multilevel supply chains.
Data Value
Corporate management acknowledges the opportunities to commercialize data. Those who manage to succeed are more likely to attract investors. What is more, corporate databases are becoming a valuable digital asset that plays a very important role in M&A processes.
Companies not only sell data to generate income but also integrate it into their products and services, use it internally to create value streams and externally to provide customers with more relevant information.
Sustainability
Environmental, social, and governance (ESG) issues have been on the rise lately, and the trend is likely to gain pace among the corporate leadership. Customers start to pay more attention not only to how much money the company generates but also by what means it is earned: no greenhouse emissions, waste-free production processes, and zero loss of feedstock are some factors for efficiency estimation.
Sampling Methods in Data Collection
The company’s target audience may consist of a large number of customers representing different groups. The task to address each of them seems impossible. Sampling helps to identify particular subgroups of the audience that reflect all the main features of the whole group. The process may be complex, but there are some statistical methods that ensure a subgroup represents the whole group in the most accurate way possible.
These sampling methods include the following.
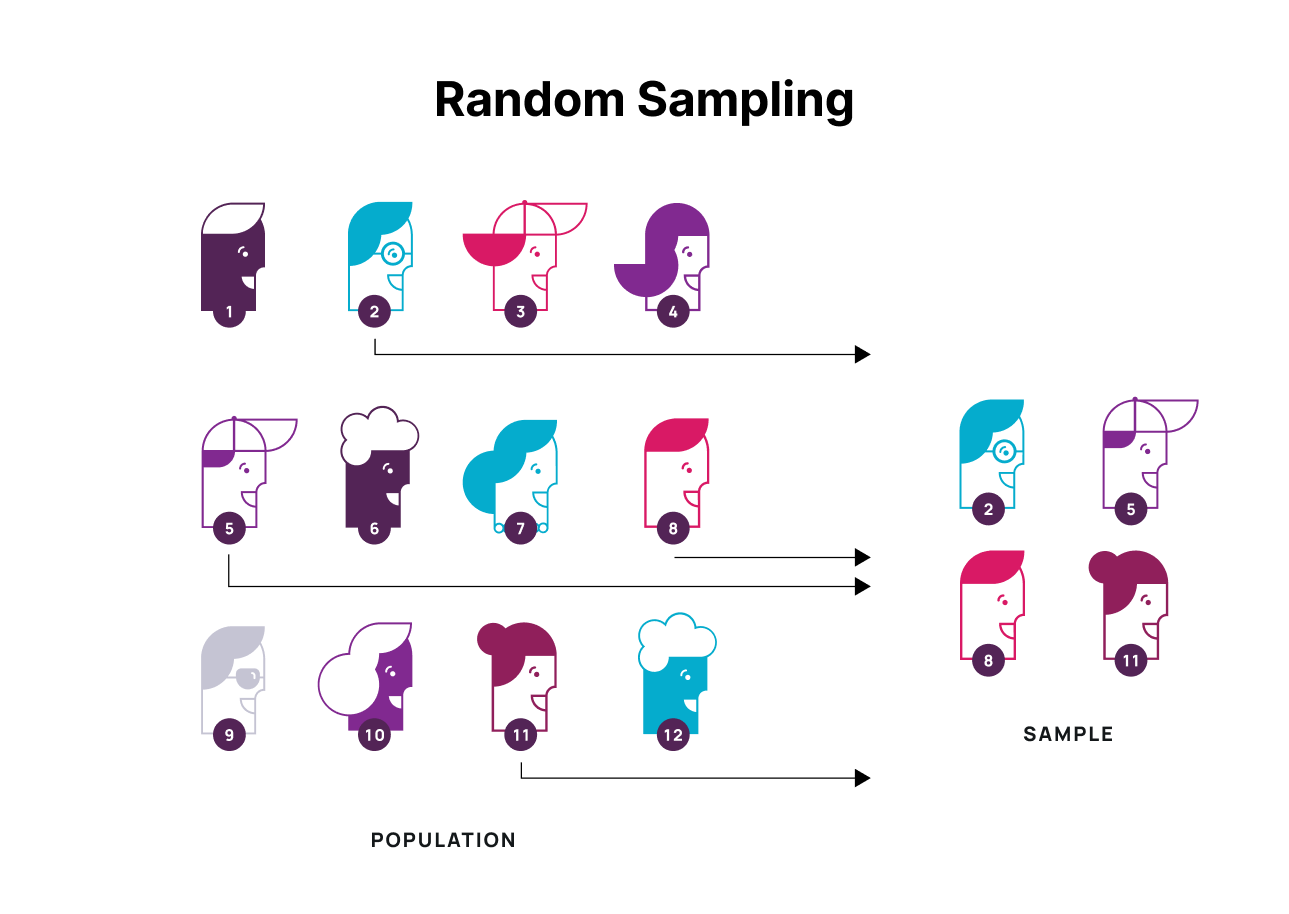
Random Sampling
Random sampling is the process of picking respondents without any pattern or system. At first glance, this method may seem unscientific, but it can be rather valuable, as it just gets rid of the elements that can decrease the validity of the research. Still, randomness requires some system. For example, if we take into consideration a popular city and start to pick people who walk on the main street on Saturday afternoon, we will get a rather diverse cross-section of tourists. But the local population will not be present, as they usually tend to avoid such areas, especially during the weekends. Computer randomizers can be a solution to this problem.
Systematic Sampling
Systematic sampling is built on the basis of some rules designed to create regularity. For example, observing every fifth customer will give the order to the process. Systematic sampling can be a rather rigid method in some cases, as the data may be irrelevant, for example, when every fifth customer turns out to be a teenager under 16 years old.

Convenience Sampling
Convenience sampling is considered to be the easiest method but, at the same time, is the least reliable. It is applied to data collection from those who are the easiest to reach. An example can be a questionnaire sent to the employees of one department instead of the whole company, which may be effort-consuming. But there are some cases when this type of sampling may be effective — for example, when it is necessary to get data on the first product impression where respondents and their diversity is of no importance.
Clustered Sampling
Clustered sampling is aimed at subgroups and not at individuals. The clusters are usually defined beforehand; for example, they can include areas or regions that participate in some research. Clustered sampling can be of two types: single-stage (when all the representatives of the cluster are included) and two-stage (when only particular representatives are chosen). The main advantage of this method is that the cluster is already clearly defined, and you don’t have to define it yourself. The only problem may occur if the cluster doesn’t represent the whole community accurately.

Stratified Sampling
Stratified sampling is applied to subgroups of a population that have similar characteristics. For example, the respondents may be divided by gender, age, education, and many other parameters. When they are clearly determined, the risk of bias decreases. But when the characteristics are not so clear, the collected data may not be very accurate. The main difference between cluster and stratified sampling is that only cluster sampling only includes certain clusters in the research process, while stratified sampling considers only the individuals from each group on a random basis.
Data Collection Tool: What is It?
A data collection tool is a software, algorithm, or some other instrument for gathering data. The success of the process is defined by choosing the most suitable tool. These tools are based on different methods of data collection. Some of them include direct questions concerning customers’ preferences, while others monitor what customers do on the webpage or how they interact with different online or offline elements.

The Best Data Collection Tools for Academic, Opinion, and Product Research
The best data collection methods for academic, opinion, and product research are described in detail in the following part of the article. Read further to learn more about them.
Interview
An interview is a personal conversation between two people that collects information for research purposes. Interviews can be structured, semi-structured, or unstructured.
- Structured interviews are just verbal questionnaires, which makes them a little superficial and not very time-consuming.
- Semi-structured interviews contain several key questions that cover the research topic in a deeper way.
- Unstructured interviews are in-depth ones and are designed to collect as much information on the subject as possible.
- Interviews offer flexibility when it comes to the level of immersion and time consumption, but they may be rather expensive to organize.
All types of recorders, including dictaphones and digital cameras, can be used for interview organization.
Questionnaire
A questionnaire is a data-collecting tool that consists of a series of questions that can cover different topics and are answered by the target audience. All the questions can be divided into three big groups: fixed-alternative, scale, and open-ended. The choice of questions is defined by the purpose and scope of the research. Questionnaires are an easy and cost-effective way to collect data sets with a variety of options for data representation. At the same time, respondents may lose interest in the middle of the questionnaire or leave some questions unanswered.
Data Reporting
The data reporting process is based on gathering information and submitting it for further analysis. The key factor of this method is using a reliable data source, as inaccurate information can lead to bad decisions. Despite the fact that data reporting can help with decision-making, results may be biased, as the source of information may present it in a subjective way, or respondents might not give detailed answers. The main sources of information for data reporting include non-governmental organizations, newspaper and website articles, and even hospital records.
Existing Data
This method introduces new information to existing data. Getting data from existing sources like archives or research journals can be a good example. The main advantage of this method is data accuracy and its easy accessibility. Still, some problems with data evaluation and understanding may occur.
Observation
As we can see from the name of this method, data is gathered through observation of the research object. The observer can be an observer, participant, or both. This method is easy to organize, it is applied practically everywhere, and the respondents don’t have to create any reports afterward. The drawbacks of observation include such factors as unpredictable validity and costly organization. The main tools for observation include checklists and direct observation.
Focus Groups
This method is applied for qualitative analysis of the object when it is necessary to collect data about the respondents’ feelings and opinions. The focus groups are offered open-ended questions in order to get feedback. This method is cost-effective, and the gathered data is usually very detailed. But bias may occur, and the outcomes are usually uncontrollable. Difficulties with assembling an inclusive group of respondents are also a common thing. The best tools to get the answers from the focus group are the following.
- Two-way. In this case, one focus group is answering the questions, while the second one listens to them and offers its own point of view on the problem to initiate further discussions afterward.
- Dueling moderator. Two moderators with opposing opinions take part in the discussion within the focus group to facilitate new ideas and points of view.
Combination Research
This data collection method applies innovative methods and demands the invitation of both individuals and groups to gather relevant responses. This research is used when it is necessary to collect qualitative data on sensitive subjects through a combination of other methods. Combination research encourages participants to collaborate on a deeper level and enriches the data. But it costs more and takes more time than all the above-described methods.
The Best Templates for Data Collection
Different templates can be applied for different customer surveys. Let’s have a look at best practices.
Customer Satisfaction
Templates for assessment of customer satisfaction give an opportunity to collect data on such aspects as what the most popular product or service is, whether the customer will recommend it or not, and whether the level of customer service is good enough.
Demographic Characteristics
Templates that assess some demographic characteristics of the customer give access to information like gender, age range, and social group breakdowns. Respondents also sometimes are asked to share their personal information or political views.
Feedback
This template is necessary to gather feedback concerning the details of the purchased product or service. It helps to assess the satisfaction level not only of the product itself but also of delivery and other important aspects.
Online Questionnaire
These templates are used for gathering large sets of data concerning respondents like gender, age, race, educational background, and so on.
The Best Method for Collecting Qualitative Data
The best method for collecting qualitative data, which relies on the feelings, views, and beliefs of the respondents, is the combination research. The main reason for this is that the method relies on interviews and focus groups, which are the most useful when it comes to sensitive data that cannot be measured in numbers.
The Best Method for Collecting Quantitative Data
The best method for collecting quantitative data is the questionnaire, as it can be cost-effective with a large number of respondents involved. The gathered data sets can be voluminous, but a unified template makes them easy to organize, visualize, and analyze. One more benefit of a questionnaire is that it gives an opportunity to compare the current data with the previously gathered information.
Data Collection and Lead Generation
Data collection and lead generation are closely connected. According to the definition of lead generation, it is the process of turning customer interest in a product or service into a sale. In marketing, this notion means collecting personal contact data (a “lead) through a particular web form. A lead is the foundation of a company’s activity.
Leads are generated with the help of different means, data collection being one of them. As more and more sales are done on the Internet, online lead generation becomes one of the most efficient methods.
Companies collect personal information such as names, email addresses, and preferences by using different online forms or by making the visitors register on the website. In exchange for that data, people are offered something valuable, like a premium account or a discount. It is necessary to provide visitors with a positive customer experience in order to make their further conversion into real customers smoother.
Gated content is another tool that makes access to personal information easier. It is demonstrated only when the visitor leaves some contact information. Without a content gate, users can surf the web page without any notifications about registration events, which would have a negative impact on sales.
A controllable lead generation process, with the help of online forms for downloadable content, is an effective way to increase the quality of the leads. But in this case, the risk of getting inaccurate data emerges, as many people nowadays have separate emails for advertising and spam letters.
In order to cope with this situation, companies may use CAPTCHA for email verification or Internet Protocol limiting to restrict the number of available downloads from a particular IP address.
Companies can also introduce social media and search engine optimization (SEO) into their marketing strategies in order to generate more leads. Social media helps engage with the potential and existing customers in a more effective way, while SEO will help promote the website in search engine results pages (SERP). Combining the above-described methods is the most effective way to generate leads.