In 2023, cloud computing keeps gaining momentum, being the key driver of many transformative tech trends. The term cloud computing refers to on-demand access to computing resources via the internet. The availability of servers, applications, development tools, data storage, and computing power enables customers to use infrastructure and applications without needing to install and maintain them on-premises. Cloud computing eliminates the need to invest in purchasing and owning the expensive infrastructure, offering it as-a-service on the cloud provider’s servers and data centers. The three most popular types of cloud service offerings include:
- Software as a Service or SaaS;
- Infrastructure as a Service or IaaS;
- Platform as a Service or PaaS.
All these types of services aren’t mutually exclusive. Many medium-sized businesses use more than one, while most large companies use all three.

Source: https://www.grandviewresearch.com/
For businesses of all sizes, cloud computing offers a range of benefits, including faster time to market, scalability, flexibility, advanced security, and significant cost savings. All the cloud computing resources are hosted on a remote data center and are managed by a cloud service vendor who provides them for a monthly subscription fee or pay-as-you-go model, billed according to usage.
In 2023, companies worldwide are expected to continue leveraging cloud services to access new innovative technologies and improve the efficiency of their operations and processes. Below, we’ve prepared some of the top cloud computing trends that are believed to have the most impact on the way companies work.
TOP cloud computing trends in 2023
Artificial intelligence and machine learning
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are provided as cloud services, as it’s a challenging and costly task for businesses to build their own AI infrastructure. Data collection and training algorithms typically require huge computing power and data storage space, and for most companies, it is a more cost-effective solution to rent as a service.
Cloud service vendors like Microsoft, Amazon, and Google are increasingly relying on AI technologies to create more efficient and cost-effective cloud services for their customers, and in 2023, we can expect to see continued innovation in AI and ML-powered cloud. These technologies can help cloud providers to manage the vast distributed networks, regulate the power and cooling systems in data centers, and implement cybersecurity solutions to keep the data safe.
Every kid coming out of Harvard, every kid coming out of school now thinks he can be the next Mark Zuckerberg, and with these new technologies like cloud computing, he actually has a shot
Multi-cloud infrastructure
If the last year was considered the year of hybrid cloud, 2023 is expected to be the year when businesses start realizing the advantages of a multi-cloud approach. This strategy refers to diversifying the services with several cloud vendors and offers a range of benefits to organizations, including enhanced security and flexibility.
A multi-cloud approach eliminates the risk of being tied to a single cloud provider and helps create redundancy, reducing the chance of system errors or downtime due to a critical business failure. While adopting a multi-cloud infrastructure, organizations are no longer tied to one cloud platform, like Azure, AWS, or Google Cloud. Instead of this, with the growing popularity of containerized apps, companies can quickly port their apps to new platforms in case of changes in service levels or more cost-effective offerings from different vendors.
Reports show that by 2023, 84% of mid-sized and 94% of large companies will adopt a multi-cloud approach, which is going to make it one of the year's defining cloud computing trends.
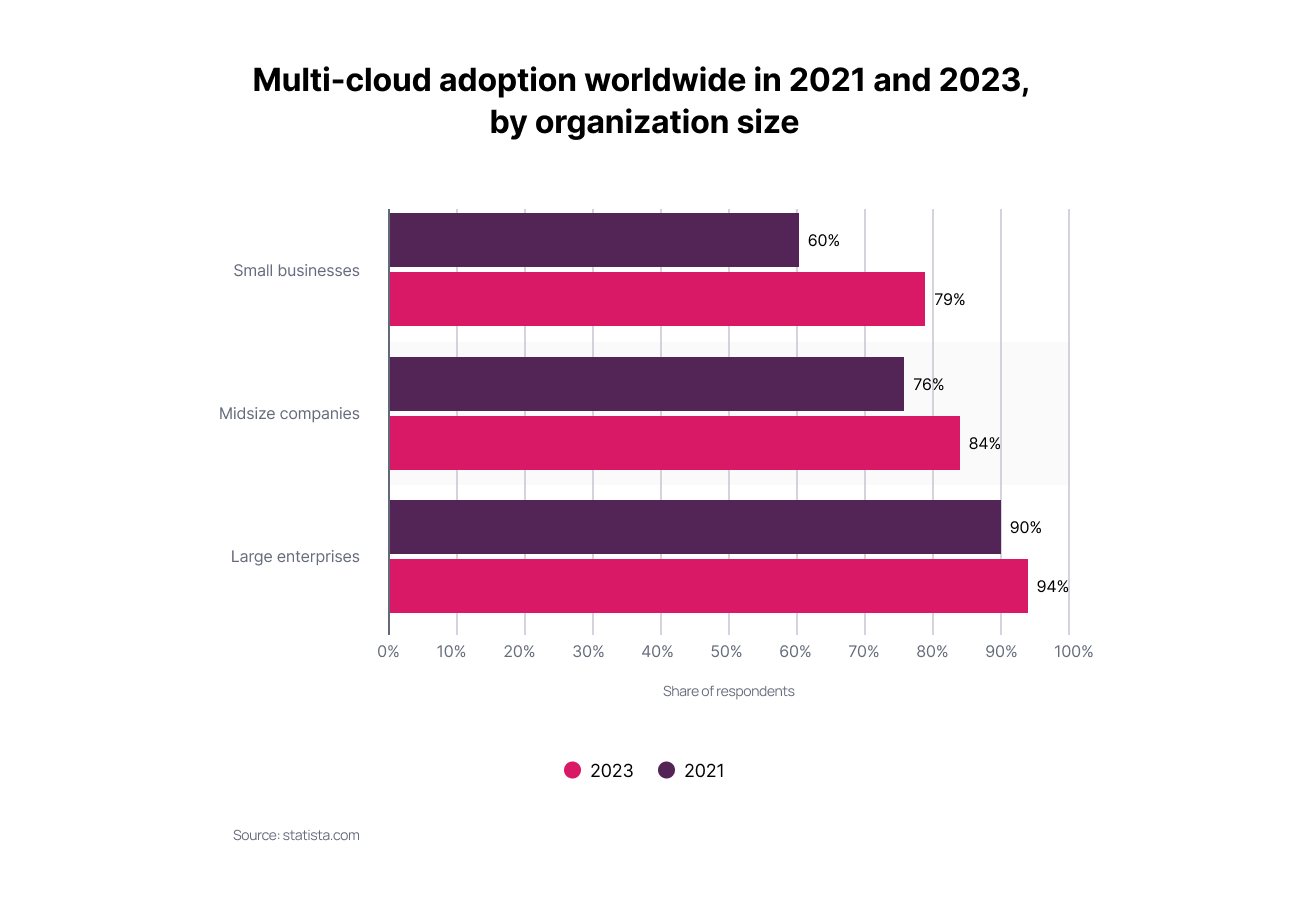
Source: https://www.statista.com/
Cloud security and resilience
Though migrating to the cloud brings numerous benefits for companies, it also entails a new level of cybersecurity threats, and security remains one of the most controversial moments in cloud adoption. To date, top cloud vendors utilize the best practices and solutions to ensure their client data is secure. These practices often include:
- Data encryption;
- Discovering and mapping the SaaS data;
- Matching controls to the risk level;
- Logging and monitoring;
- Integration with Identity and Access Management (IAM) tools;
- Using a safe security-prioritized Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC);
- Using key vault services;
- SaaS Security Posture Management (SSPM).
In 2023, spending on cyber security and building resilience is expected to rise, with cloud providers implementing innovative and cost-efficient solutions for maintaining cyber security. It may include increased use of AI and predictive technologies to detect threats before they cause problems and increased use of managed “security-as-a-service” providers.
Cloud gaming
Leading cloud providers like Sony, Microsoft, Nvidia, and Amazon continue to invest in streaming gaming services, and this tendency is expected to increase in 2023 with the ongoing rollout of 5G. Streaming video games require higher bandwidth than music or videos, so with 5G and other ultra-fast networking technologies projected to rise this year, cloud gaming is expected to make an impact. According to Google, the technology that powers Stadia will form the basis of a B2B game streaming service, allowing game developers to provide streaming functionality directly to their customers.
Low-code and no-code cloud services
Low-code and no-code solutions include tools for building web apps and websites and designing almost any digital solutions companies may need. Low-code and no-code solutions are also becoming available for building AI-powered apps, significantly lowering barriers to entry for organizations looking to leverage AI and ML technologies.
Low-code and no-code tools like Zoho, Fligma, and Airtable are available via the cloud, allowing users to access them as-a-service without the need to run their computing infrastructure. These solutions enable users to carry out tasks that previously would have required coding experience, like building web applications, designing websites, and automating spreadsheet tasks. Low-code and no-code cloud services are projected to grow and become increasingly helpful in 2023 and beyond.
SaaS, IaaS, and PaaS in cloud computing
The cloud remains a hot topic for businesses of all sizes, providing them with benefits like cost reduction, continuous software updates, unrivaled security, flexibility, and scalability. With the growing global adoption of cloud computing solutions, enterprises worldwide have already switched their businesses to the cloud or are on the way to considering this option. When you start considering migrating your business to the cloud, whether deploying applications or infrastructure, it is critical to understand the differences between different cloud service models and the pros and cons each model can bring to you.
Cloud computing is about how you do computing, not where you do computing
Generally, as-a-service refers to how IT assets are used in these offerings and to the significant differences between traditional IT and cloud computing. In the case of traditional IT, an organization consumes IT resources like software, hardware, development tools, and applications. The company buys, installs, manages, and maintains these assets in its on-premise data center. At the same time, in cloud computing, it’s the cloud provider's responsibility to manage, update, and maintain assets, with customers consuming them via the internet and paying for the services on a subscription or pay-as-you-go basis.
The number of as-a-service types keeps constantly growing, although there are usually three most popular types of cloud service offerings to compare:
- SaaS, or software-as-a-service;
- IaaS, or infrastructure-as-a-service;
- PaaS, or platform-as-a-service.

Source: https://www.t4.ai
Our review will examine the main characteristics, delivery, pros and cons, and examples for each model. It will help you understand the critical differences between these types of cloud services and choose the one that best fits the needs and goals of your business.
Software as a service
In 2022, software as a service or SaaS occupied the largest cloud computing market share of 36.8%, remaining the most popular type of cloud service solution. This model represents cloud-hosted, ready-to-use application software.
SaaS characteristics
In SaaS architecture, the application and all the infrastructure needed to deliver it, such as storage, servers, networking, application software, and middleware, is hosted and managed by the SaaS provider. SaaS vendors manage all software updates and ensure a level of availability, security, and performance as part of the service level agreement (SLA). It eliminates the need for IT review and streamlines business processes. The main features of the SaaS platform include:
- Accessibility over the internet;
- Platforms are hosted on a remote server and managed by a third-party service provider;
- Customers aren’t responsible for hardware or software updates;
- Different tiers for small, medium and enterprise-level businesses.
SaaS delivery
Software as a service model is delivered as a fully functional service and can be accessed via any web browser without downloading and installing applications. SaaS users connect to the app through API or dashboard and rely on the service provider in the case of technical issues, bug fixes, support, middleware, and updates.
SaaS advantages
- Simplicity. Within the SaaS model, you offload all infrastructure and app management to the service vendor. All you have to do is create an account, pay the subscription fee, and start using the app, while the provider will handle everything else.
- Minimal financial risk. Many software as a service vendors offer a free trial period or low monthly fee for the first month, allowing you to see if the product meets your needs.
- Cost reduction. The license SaaS costs are lower compared to traditional methods, while the pay-as-you-go pricing model allows customers to pay based on how much they use.
- Scalability. SaaS solutions can be easily scaled up or down depending on your business needs. You can easily add new users and purchase more data storage.
Many SaaS solutions are integrated with other SaaS offerings, so you don’t have to purchase another server or software. Some service providers also allow you to customize your product by providing a companion PaaS solution, such as, for example, Heroku - a PaaS solution for Salesforce.
SaaS concerns & limitations
The SaaS cloud computing model also has some potential drawbacks, some of that include:
- Security risks. Due to the sheer amount of data when communicating with external servers, security and compliance can be compromised. Unmanaged SaaS apps could also have potential security gaps.
- Limited control. While the cloud vendor manages all the infrastructure, users have limited control over performance, functionalities, downtime, and how their data is managed.
- Interoperability. Integrations with existing applications and services can be challenging as many SaaS apps aren’t designed for open integrations.
- Limited customization. SaaS typically allows minimal customization when it comes to features and capabilities.
- Performance. In the SaaS model, you rely on the service vendor to maintain the service’s security and performance. Planned and unplanned maintenance, cyberattacks, or network issues can affect the performance of a SaaS app despite having adequate SLA protection.
SaaS examples
- Salesforce;
- HubSpot;
- Google Workspace;
- Slack;
- Netflix;
- Zoom;
- Adobe Creative Cloud;
- Dropbox;
- SAP Concur;
- Cisco WebEx.
When to choose a SaaS model?
SaaS is an excellent choice for small companies or startups that want an app to run smoothly and reliably but don’t have the resources to develop their own software apps. SaaS is the easiest and quickest solution for a wide range of projects, from e-commerce to short-term, and if you don’t need a highly customizable app or apps that aren’t used regularly, it’s a great option.
Platform as a service
Platform-as-a-service or PaaS model allows you to run, develop, and manage applications, providing all the necessary tools for a complete software development cycle tailored to the individual needs of an organization. It’s often easier and cheaper than building an app from scratch. The cloud services provider hosts, manages, and maintains all the software and hardware of the platform, while the developers can maintain the application management.
PaaS delivery
There are three types of delivery for PaaS platforms:
- Public. In a public cloud service, the vendor provides the servers, storage, O/S, middleware, and other features necessary for the app deployment, while the user has limited configuration options.
- Private. This type of cloud service offers the best security of all these options keeping the agility benefits of the public PaaS. In a private PaaS, the vendor delivers the solution within the user’s firewall, which is more commonly managed on the organization’s on-premise infrastructure.
- Hybrid. These PaaS solutions are highly flexible as they combine the benefits of public and private types and offer the ability to own internal infrastructure in private PaaS.
PaaS delivery can be compared to the SaaS delivery model. The only difference between these types is that in PaaS, users get access to an online software creation platform rather than online software, as with SaaS.
PaaS characteristics
Development or DevOps teams access the PaaS through a graphical user interface (GUI), where they can collaborate on their work across all the application lifecycle stages, including coding, integration, testing, delivery, deployment, and feedback. PaaS is designed to automate Ops and focus on Dev and is responsible for:
- Providing servers, networks, and storage.
- Providing middleware services, such as database, cache storage, and messaging.
- Bootstrapping and deploying services, including installing and configuring the OS, installing the necessary runtime and security patches and keeping them up to date.
PaaS can be accessible to several users via the same development application, and its resources can be scaled up or down depending on your business needs.
PaaS advantages
- Cost-effectiveness. PaaS pricing is usually between SaaS and IaaS, which makes it a simple and cost-effective solution for developing and deploying apps.
- Migration. With the PaaS model, you can easily migrate to a hybrid cloud model.
- Functionality. PaaS has more advanced functionality than SaaS, providing middleware and hardware for advanced tasks.
- Adaptation. PaaS supports different programming languages, allowing you to adapt easily to the model language.
- Scalability. PaaS solutions can be easily adjusted to a developer’s needs.
- Time-to-market. The model eliminates the need to set up an entire infrastructure, making integration easier and quicker.
The PaaS model offers users focus on the tasks at hand, leaving all the back-end processes to the cloud vendor. It also allows your development teams to write much less code than before.
PaaS concerns & limitations
- Limited control. The cloud vendor manages and controls the vast majority of back-end processes.
- Security issues. Entrusting all the data to the third-party PaaS provider poses security risks and concerns for your business and end-users.
- Vendor lock-in. PaaS-developed software is dependent on it for future updates, so it may be difficult to migrate your projects to other vendors. Some elements can also be incompatible with the cloud platform.
- Integration. If not every component of a legacy IT system is built to run in the cloud, integrating with existing services and infrastructure can be a challenge.
- Operational limitations. PaaS tends to limit operational capabilities for end users, and customized cloud operations with management automation workflows may not be applicable to PaaS solutions.
PaaS examples
- Microsoft Azure;
- SAP Cloud;
- AWS Lambda;
- Heroku;
- Google App Engine;
- IBM Cloud Foundry.
When to choose a PaaS model?
The PaaS model can accelerate and simplify software development at any level. It’s a good choice when you have a particular development task that doesn’t require infrastructure or want to test an idea with a potential project. This model is also good for IoT application development and real-time data processing from IoT devices, API development and management, and cloud-native development.

Source: https://www.plesk.com/
Infrastructure as a service
The IaaS model offers you virtualized computing resources, such as storage, servers, and networking, that can completely replace on-premises infrastructure. Infrastructure as a service is highly scalable and offers businesses flexibility, cost reduction, and complete control over computing infrastructure. It is also the most secure and scalable model out of the three.
IaaS delivery
With infrastructure as a service, the client manages apps, O/S, runtime, middleware, and data, while the IaaS vendor is responsible for all other parameters. All the resources are accessed through virtualization technology via a graphical dashboard or programmatically through API. IaaS customers can choose between servers on unshared physical hardware or virtual machines hosted on shared physical hardware. In the latter case, virtualization is managed by the cloud service provider.
IaaS characteristics
IaaS provides on-demand access to cloud-hosted computing infrastructure, which customers can provide, configure, and use in much the same way they use on-premise hardware. IaaS users get access to the hardware via the internet and pay for the resources used on a subscription or pay-as-you-go basis. This model is quite popular among organizations and IT administrators that don’t want to invest in expensive hardware and want to retain complete control over the infrastructure.
IaaS advantages
- Control. The IaaS model offers customers complete control over the entire infrastructure.
- Flexibility. IaaS is the most flexible model out of the three. It allows you to experiment with all your projects without creating the on-premises infrastructure.
- Scalability. The model is highly scalable. You don’t have scalability limits and can easily upscale or downscale them according to your needs.
- Security. As you’re the one who can access your data stored on IaaS, you get more advanced security and protection compared to other cloud computing models.
- Availability. The IaaS model allows you to create redundant servers to ensure availability during local power outages, physical disasters or other issues.
- Automation. With IaaS, you can easily automate the storage, servers, and networking deployment.
IaaS concerns & limitations
- Costs. The IaaS model is the most expensive out of the three at a basic level.
- Poor support of legacy applications. Often, cloud infrastructures aren’t designed for this functionality. Minor enhancements to legacy apps may be required before migrating them to the cloud.
- Responsibility. With IaaS, you’re responsible for maintaining the virtual machine with all its components.
- Multi-tenant security. Customers must rely on the vendor to ensure that virtual machines are adequately isolated within the multi-tenant cloud architecture, as the hardware resources are dynamically allocated to users as they become available.
IaaS examples
- DigitalOcean;
- AWS;
- Microsoft Azure;
- Google Compute Engine;
- Linode;
- Rackspace.
When to choose an IaaS model?
The IaaS model will be a good choice for small companies and startups who want to save time and resources on purchasing and creating on-premises software and hardware. At the same time, larger companies can also benefit from IaaS due to the complete control over the apps and infrastructure this model provides. Also, if your company is experiencing rapid growth, the IaaS approach will be the best as it offers high scalability, allowing you to change software and hardware according to your growing needs quickly.
Designing a Comprehensive Security Strategy for IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS: Best Practices
As organizations embrace the benefits of cloud computing models, they also encounter specific security risks inherent to each model. Gaining insights into these risks is crucial for implementing effective security measures. Below, we’ve collected an overview of the main security risks associated with each cloud computing model.
SaaS Security Risks
Data breaches. SaaS apps store vast amounts of sensitive user data. Inadequate security controls or compromised credentials can lead to unauthorized access and data breaches. Lack of control. Organizations using SaaS have limited control over application security settings, updates, and configurations, as these are managed by the provider. Account hijacking. Weak authentication mechanisms or phishing attacks can lead to unauthorized individuals gaining access to user accounts, potentially resulting in data loss or manipulation. Data loss. Users might mistakenly delete or overwrite data in SaaS applications, and in some cases, there might not be adequate backup mechanisms in place. Vendor lock-in. SaaS users might mistakenly delete or overwrite data in the applications, and in some cases, there might not be adequate backup mechanisms in place.
PaaS Security Risks
Insecure APIs. PaaS platforms expose APIs that developers use to build and deploy applications. If these APIs are not properly secured, they can become entry points for attackers. App vulnerabilities. Developers might inadvertently introduce vulnerabilities into applications built on PaaS platforms, such as SQL injection or cross-site scripting (XSS). Data leakage. Applications sharing the same PaaS platform might accidentally access or leak each other's data due to inadequate isolation mechanisms. Dependency risks. Organizations relying heavily on a PaaS provider are vulnerable to disruptions if the provider experiences downtime or goes out of business. Limited customization. PaaS platforms offer pre-configured environments, which might limit the ability to implement certain security controls tailored to specific needs.
IaaS Security Risks
Misconfiguration. In IaaS, organizations configure their virtual resources, making misconfigurations a significant risk. Incorrectly configured firewalls, access controls, or authentication mechanisms can lead to data exposure. Shared environment risk. Since multiple users share the same underlying infrastructure, vulnerabilities in one user's setup can potentially impact others. Data loss. While cloud providers typically offer reliable storage solutions, data loss can still occur due to mismanagement, accidental deletion, or hardware failures. Insider threats. Organizations may face insider threats from employees or contractors with access to the IaaS environment, potentially leading to unauthorized access or data breaches. DDoS attacks. IaaS resources are susceptible to DDoS attacks that can overwhelm the network, causing service disruption. Data residency and compliance. Depending on the jurisdiction in which the IaaS provider's data centers are located, data residency and compliance challenges could exist.
Addressing these security risks requires a combination of technical solutions, policies, and practices tailored to the specific cloud model. Organizations should adopt a proactive and comprehensive approach to security, considering encryption, access controls, monitoring, regular audits, employee training, and continuous risk assessment to safeguard their digital assets, maintain operational integrity, and preserve customer trust.
Designing a Comprehensive Security Strategy for IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS: Best Practices
Securing cloud services demands a well-rounded strategy to mitigate risks and protect sensitive data. Creating a robust security strategy tailored to the intricacies of SaaS, IaaS, and PaaS environments is not just a prudent measure but a pivotal one, as it not only fortifies the digital fortresses of these businesses but also paves the way for uninterrupted growth and fortified customer trust. This section of our article presents a step-by-step guide to crafting a robust security approach.
Assess Your Data and Needs
Understand the nature of the data you'll be handling and the compliance requirements specific to your industry. Determine which cloud service models (IaaS, PaaS, SaaS) you'll utilize and to what extent.
Vendor Evaluation
Research and select reputable providers with robust security protocols and ensure they comply with industry standards and regulations. Also, review their security documentation, certifications, and data protection practices.
Data Classification
Categorize your data based on sensitivity levels. It aids in defining access controls, encryption requirements, and data handling processes for each data type.
Access Control
Implement a robust access management system. You can utilize techniques like Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA), role-based access control (RBAC), and just-in-time access to limit unauthorized entry.
Encryption
Encrypt data at rest and in transit. Implement encryption mechanisms provided by the cloud provider and consider using your own encryption tools for an added layer of security.
Network Security
Configure firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and intrusion prevention systems to monitor and control network traffic. Segment networks to prevent lateral movement of threats.
Patch Management
Keep all systems and applications updated with the latest security patches. Automate the patching process to minimize vulnerabilities.
Application Security
Secure applications through code reviews, vulnerability assessments, and penetration testing. Utilize web application firewalls (WAFs) for added protection against web-based attacks.
Monitoring and Logging
Set up continuous monitoring to detect suspicious activities. Employ centralized logging and analysis tools to identify anomalies and respond swiftly to potential breaches.
Incident Response Plan
Develop a detailed incident response plan. Define roles, responsibilities, escalation procedures, and communication protocols to manage security incidents effectively.
Backup and Recovery
Regularly back up data and test the restoration process. It ensures you can quickly recover your systems and minimize downtime in case of data loss or breaches.
User Training
Educate users about best practices for cloud security, including password hygiene, phishing awareness, and the proper use of cloud resources.
Regulatory Compliance
Ensure your cloud security strategy aligns with relevant regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, or industry-specific standards.
Continuous Improvement
Regularly assess your security strategy to identify weaknesses and emerging threats. Adapt your approach to address new challenges as they arise.
By following these steps and tailoring them to your organization's unique requirements, you can design a comprehensive security strategy that effectively safeguards your IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS deployments. This proactive approach empowers your business to confidently navigate the intricate landscape of cloud services, ensuring the integrity of your data, the continuity of your services, and the preservation of your customers' trust without compromising on the paramount aspect of security.
SaaS vs. PaaS vs. IaaS. Making a final decision

SaaS vs. PaaS
PaaS allows you to build apps on top of your existing network, allowing you to leave infrastructure management to the service vendor and focus on app development. At the same time, SaaS solutions are entirely managed by the provider and are ready to use. How to decide which model to choose? If you want to deploy apps with composable services rapidly and don’t mind the vendor’s lock-in, choose PaaS. This service model will provide you with all the tools you would need to succeed.
SaaS vs. IaaS
With SaaS, you get the most service from the provider in terms of software management and maintenance, while IaaS gives you maximal flexibility, scalability, and control. Choosing between these two options depends on what you want to achieve. If you want ease of use and don’t need much flexibility and scalability, SaaS will be a better choice saving you time and money.
PaaS vs. IaaS
IaaS offers you maximal control over your app and infrastructure in general, while with PaaS, you can trust the management of the operating system, runtime, storage, servers, virtualization, and network to a service provider. If you want complete control of your application and environment, are not limited in budget, and are ready to take responsibility for maintaining a virtual machine with all its components, IaaS is exactly what you need.
On-premise vs. SaaS vs. IaaS vs. PaaS. Transportation analogy
- On-premise solution. You own a car and are fully responsible for its maintenance and upgrades.
- SaaS solution. You share the ride with other passengers on a bus, saving money and taking no responsibility for its maintenance.
- PaaS solution. You use a taxi, can choose between a basic car or a limousine and tell the driver where you want to go.
- IaaS solution. You lease a car, can drive it wherever you want and upgrade to a bigger option if needed. You also take the whole responsibility for its maintenance.
Main differences between models
| Model | SaaS | PaaS | IaaS |
|---|---|---|---|
| User manages | Applications, data. | Applications, data, runtime, middleware, O/S. | |
| Service vendor manages | Applications, data, O/S, runtime, middleware, servers, storage, virtualization, networking. | Runtime, O/S, middleware, servers, storage, networking, virtualization. | Servers, storage, visualization, networking. |
| Mobile technologies | Mobile commerce apps, M-payment apps, mobile social apps, mobile learning apps. | SMS API, mobile cloud apps, mobile app development, mobile agents. | Software-defined radio networks. |
| General users | Business users | Developers and deployers | System managers |
| Big Data | Data analysis, visualization. | Map-reduce API | Environment for mongoDB projects, environment for Hadoop projects |
| Internet of Things | Software for smart device management. | API for wearable computing and context-aware apps and for accessing sensor data. | Smart environments, software-defined wireless sensor networks |
| IT management | Project management software, CRM software. | Salesforce PaaS, Heroku PaaS | Cloud management |
| Operational cost | Minimal | Lower | Highest |
| Security | Requires transparency in service vendor’s security policies | Additional security is required | You should take into account the compliance of the policy of virtual and physical servers. |
| Portability | No portability | Lower | Best |
| Business scenarios to use | Email, CRM, ERP software, billing and invoicing systems, website testing, office automation, virtual desktop, HR/HRM apps. | App deployment, CI/CD automation, container orchestration, auto-scaling & clustering. | Website or app hosting, IT administration purposes, complex data analysis, virtual data centers. |
| Best for | Startups or small businesses who can't develop their own software apps; apps that aren’t used regularly; personal use. | Mid-sized companies that don't need to invest in IaaS; software development at any level; customized apps. | Startups and small companies who want to save time and money; rapidly growing companies, large companies who want to get complete control over the infrastructure. |
SaaS with Brocoders. Why choose us?
If you’re ready to follow 94% of enterprises and move to the cloud, you need to do this wisely. Great SaaS products are all simple, although developing new software as a service solution holds a myriad of challenges. It may be a lack of understanding of the SaaS business model, not knowing your market and how to price your product, missing SaaS development expertise, and many other pitfalls that typically entail the development of a SaaS-based product. To save time, effort and resources, you need a team of experts who will bring your business idea to life and never miss a single important step. And we’re here to help you.
Why Brocoders? With 8 years of experience building web-based and mobile-based products, we know how to identify potential problems and add genuine value to your project. With a deep knowledge of SaaS technology and 87 top specialists on board, we’ll help you to:
- Develop a SaaS product your customers will love;
- Avoid common SaaS pitfalls;
- Achieve long-term success;
- Grow your customer base.
We work in 22 time zones to fully adapt to your schedule and integrate perfectly into your in-house team. If you’re a SaaS product owner, we can collaborate in three ways:
- Develop a functional MVP;
- Scale your existing SaaS product;
- Augment your team with our qualified SaaS app developers.
Brocoders has a 5.0 rating on Clutch, continuing to receive honest and objective feedback from our clients. We keep growing and improving to arrange the development smoothly and beneficially. If you want to set up a skilled SaaS development team and start your SaaS project without delays, visit our website today or book a call with our digital business expert.
Wrapping up
Cloud computing keeps gaining momentum, and new models emerge next to SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS. Communication-as-a-service (CaaS), function-as-a-service (FaaS), monitoring-as-a-service (MaaS), and even everything-as-a-service (XaaS) might be of interest to you and bring more benefits to your business in the near future. All these models are designed for companies looking for specific services to stay competitive in the continuously evolving cloud market.
Each cloud computing model reviewed in our article offers specific features and functionalities. It’s crucial for your business to understand the differences between the cloud models and choose the one that fits your needs, goals, and resources best. Try to decide what is more important for your company - convenience, customization or control. Think about the plans for the future - how fast do you expect your business to grow? How much scalability will you need in the future? And finally, how limited are your financial resources? Once you’ve got answers to all these questions, find the right vendor that fits your organization's culture and will help improve the productivity and efficiency of your teams.

